Gnotobiologie

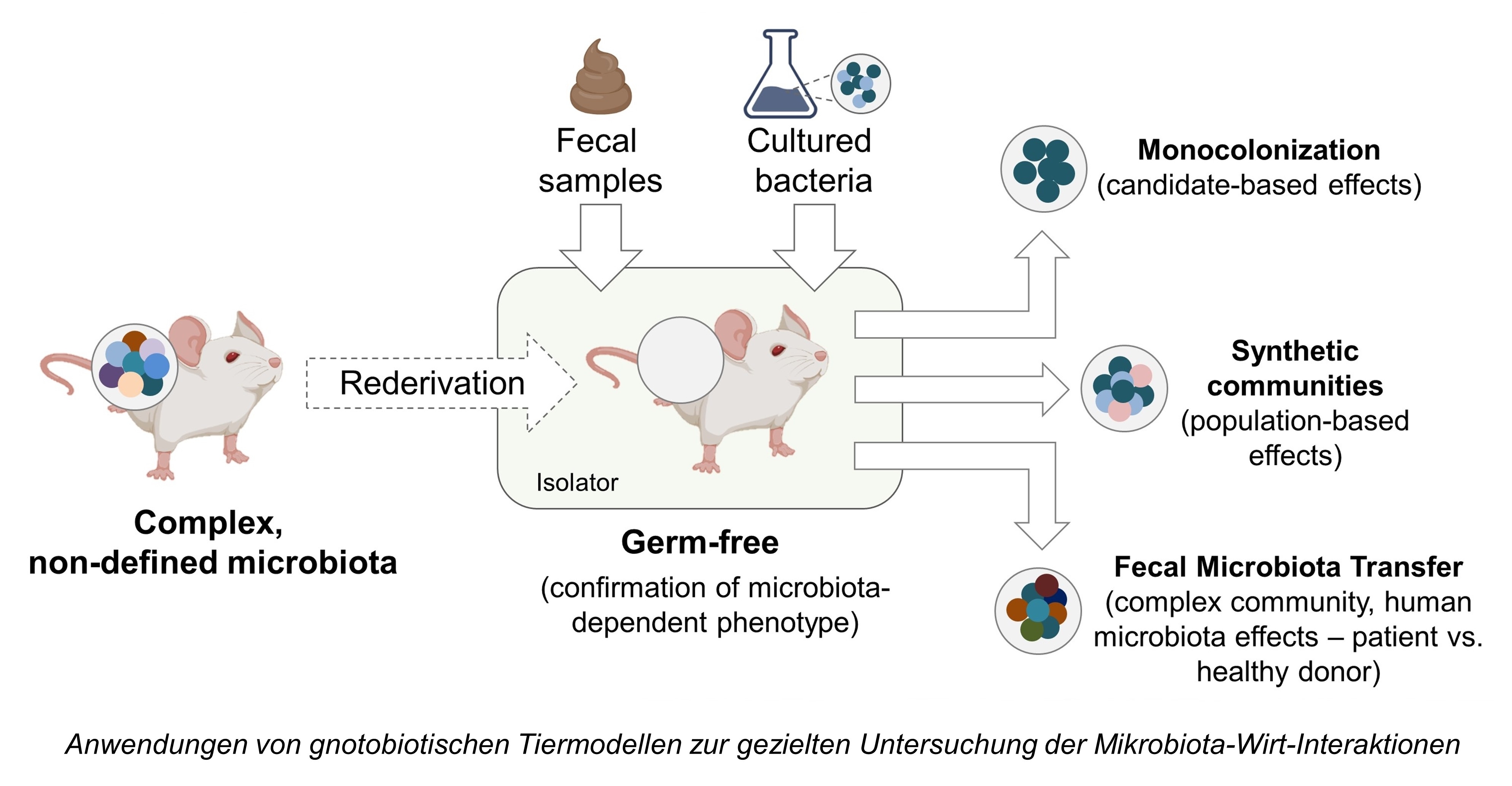
Die Darmmikrobiota ist ein hochkomplexes Ökosystem aus Mikroorganismen (Bakterien, Archaeen, Pilze und Viren), die für die Gesundheit des Wirtes von großer Bedeutung sind. Diverse Erkrankungen des Menschen werden mit Veränderungen der mikrobiellen Zusammensetzung und Funktion der Mikrobiota in Verbindung gebracht. Hierbei stellen gnotobiotische Tiere ein wertvolles Versuchsmodell dar, um die Funktion und den Einfluss von Darmmikroben unter homöostatischen und pathologischen Bedingungen zu untersuchen. Der Begriff "gnotobiotisch" bezeichnet einen vollständig bekannten mikrobiellen Status von Organismen. Diese Definition schließt sowohl keimfreie Tiere ein, die frei von allen lebenden Mikroorganismen sind, als auch Tiere, die mit spezifischen Mikroben gezielt besiedelt sind. Die aus diesen Modellen gewonnenen Erkenntnisse können zu einer erheblichen Verbesserung der Prävention, Diagnose und Therapie von einer Vielzahl an Erkrankungen führen. Um ihren strikten Hygienestatus aufrecht zu erhalten, werden gnotobiotische Nager in speziellen Tierhaltungseinheiten, wie z.B. Isolatoren, artgerecht gehalten.
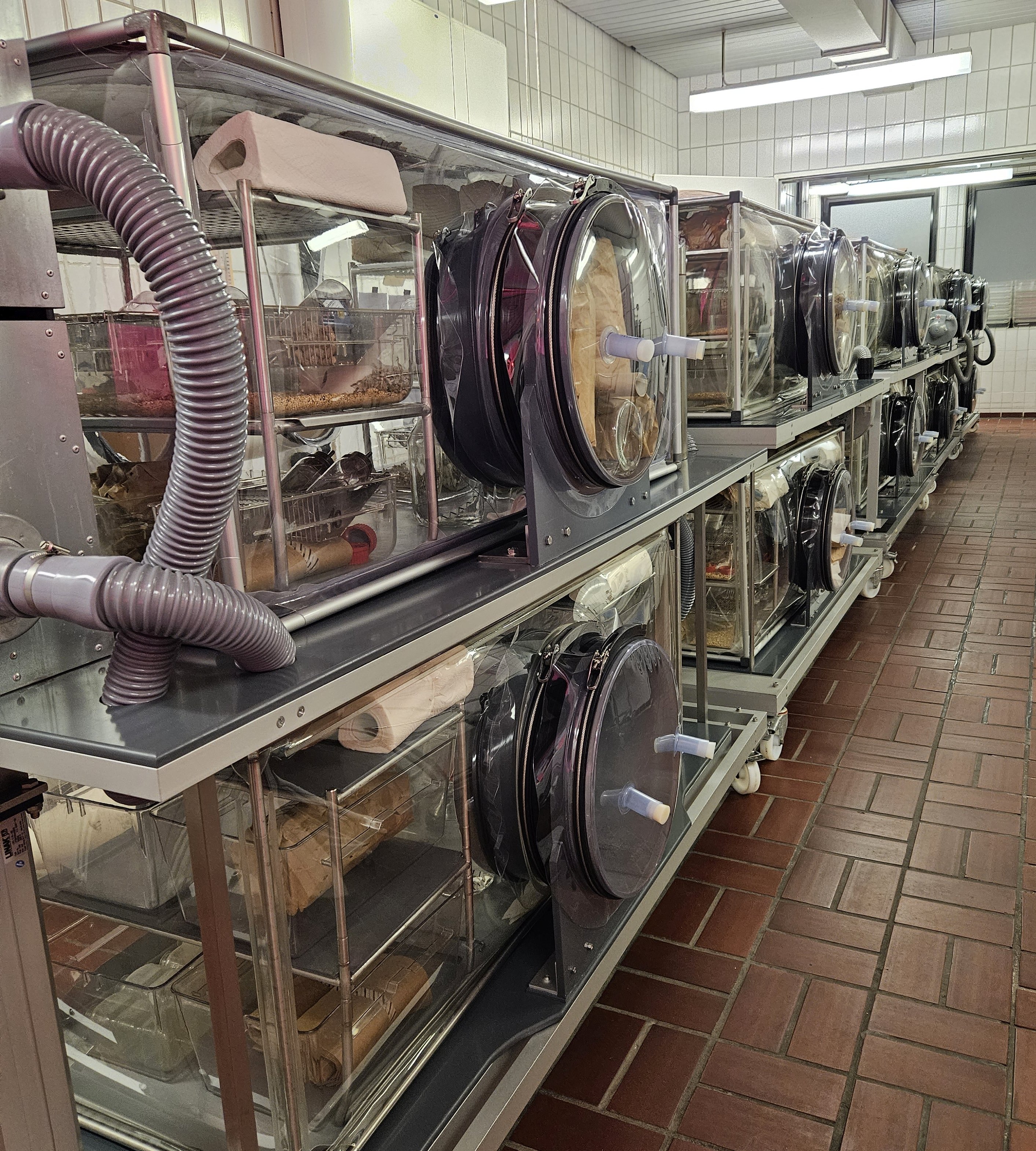
Die Abteilung für Gnotobiologie des Zentralen Tierlaboratoriums ist eine voll ausgestattete, moderne gnotobiotische Einrichtung, die in den frühen 1980er Jahren gegründet wurde und auf eine lange Tradition hinsichtlich der Arbeit mit gnotobiotischen Nagetiermodellen zurückblickt. Diese Expertise wurde bereits erfolgreich in nationale und internationale Verbundforschungsprojekte eingebracht. Derzeit verfügt die gnotobiotische Einrichtung über 36 Isolatoren, 50 Mikroisolatoren auf Käfigebene und mehr als 20 gnotobiotische Nagetiermodelle (gentechnisch veränderte Mauslinien und Wildtypstämme).
Service & Forschungsbeitrag
- Generierung von keimfreien Nagetiermodellen
- Haltung und Zucht von gnotobiotischen Nagetieren unterschiedlicher Linien
- Beratung und Hilfestellung bei der Planung von Studien mit gnotobiotischen Mäusen
- Unterstützung bei der Durchführung von kollaborativen Experimenten unter gnotobiotischen Bedingungen
- Schulungen im Bereich gnotobiotische Arbeitstechniken und Methoden
- Versand von gnotobiotischen Mäusen
- Bolsega, S., Smoczek, A., Meng, C., Kleigrewe, K., Scheele, T., Meller, S., Glage, S., Volk, H.A., Bleich, A., and Basic, M. (2023). The Genetic Background Is Shaping Cecal Enlargement in the Absence of Intestinal Microbiota. Nutrients 15. DOI: 10.3390/nu15030636
- Yin, Y., Sichler, A., Ecker, J., Laschinger, M., Liebisch, G., Horing, M., Basic, M., Bleich, A., Zhang, X.J., Kubelsbeck, L., Plagge, J., Scherer, E., Wohlleber, D., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Steffani, M., Stupakov, P., Gartner, Y., Lohofer, F., Mogler, C., Friess, H., Hartmann, D., Holzmann, B., Huser, N., and Janssen, K.P. (2023). Gut microbiota promote liver regeneration through hepatic membrane phospholipid biosynthesis. J Hepatol 78, 820-835. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.12.028
- Metwaly, A., Jovic, J., Waldschmitt, N., Khaloian, S., Heimes, H., Hacker, D., Ahmed, M., Hammoudi, N., Le Bourhis, L., Mayorgas, A., Siebert, K., Basic, M., Schwerd, T., Allez, M., Panes, J., Salas, A., Bleich, A., Zeissig, S., Schnupf, P., Cominelli, F., and Haller, D. (2023). Diet prevents the expansion of segmented filamentous bacteria and ileo-colonic inflammation in a model of Crohn's disease. Microbiome 11, 66. DOI: 10.1186/s40168-023-01508-y
- Enderes, J., Neuhaus, H., Basic, M., Schneiker, B., Lysson, M., Kalff, J.C., and Wehner, S. (2023). Microbiota-dependent presence of murine enteric glial cells requires myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88 signaling. J Biosci 48.
- Afrizal, A., Jennings, S.A.V., Hitch, T.C.A., Riedel, T., Basic, M., Panyot, A., Treichel, N., Hager, F.T., Wong, E.O., Wolter, B., Viehof, A., von Strempel, A., Eberl, C., Buhl, E.M., Abt, B., Bleich, A., Tolba, R., Blank, L.M., Navarre, W.W., Kiessling, F., Horz, H.P., Torow, N., Cerovic, V., Stecher, B., Strowig, T., et al. (2022). Enhanced cultured diversity of the mouse gut microbiota enables custom-made synthetic communities. Cell Host Microbe 30, 1630-1645 e1625. DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2022.09.011
- Agamennone, V., Abuja, P.M., Basic, M., De Angelis, M., Gessner, A., Keijser, B., Larsen, M., Pinart, M., Nimptsch, K., Pujos-Guillot, E., Schlicht, K., Sharon, I., Untersmayr, E., Laudes, M., Pischon, T., Bouwman, J., and On Behalf Of The, C. (2022). HDHL-INTIMIC: A European Knowledge Platform on Food, Diet, Intestinal Microbiomics, and Human Health. Nutrients 14. DOI: 10.3390/nu14091881
- Basic, M., Dardevet, D., Abuja, P.M., Bolsega, S., Bornes, S., Caesar, R., Calabrese, F.M., Collino, M., De Angelis, M., Gerard, P., Gueimonde, M., Leulier, F., Untersmayr, E., Van Rymenant, E., De Vos, P., and Savary-Auzeloux, I. (2022). Approaches to discern if microbiome associations reflect causation in metabolic and immune disorders. Gut Microbes 14, 2107386. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2107386
- Kini, A., Zhao, B., Basic, M., Roy, U., Iljazovic, A., Odak, I., Ye, Z., Riederer, B., Di Stefano, G., Romermann, D., Koenecke, C., Bleich, A., Strowig, T., and Seidler, U. (2022). Upregulation of antimicrobial peptide expression in slc26a3-/- mice with colonic dysbiosis and barrier defect. Gut Microbes 14, 2041943. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2041943
- Bolsega, S., Bleich, A., and Basic, M. (2021). Synthetic Microbiomes on the Rise-Application in Deciphering the Role of Microbes in Host Health and Disease. Nutrients 13. DOI: 10.3390/nu13114173
- Hinrichsen, F., Hamm, J., Westermann, M., Schroder, L., Shima, K., Mishra, N., Walker, A., Sommer, N., Klischies, K., Prasse, D., Zimmermann, J., Kaiser, S., Bordoni, D., Fazio, A., Marinos, G., Laue, G., Imm, S., Tremaroli, V., Basic, M., Hasler, R., Schmitz, R.A., Krautwald, S., Wolf, A., Stecher, B., Schmitt-Kopplin, P., et al. (2021). Microbial regulation of hexokinase 2 links mitochondrial metabolism and cell death in colitis. Cell Metab 33, 2355-2366 e2358. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.11.004
- Strigli, A., Gopalakrishnan, S., Zeissig, Y., Basic, M., Wang, J., Schwerd, T., Doms, S., Peuker, K., Hartwig, J., Harder, J., Honscheid, P., Arnold, P., Kurth, T., Rost, F., Petersen, B.S., Forster, M., Franke, A., Kelsen, J.R., Rohlfs, M., Klein, C., Muise, A.M., Warner, N., Nambu, R., Mayerle, J., Torok, H.P., … Bleich, A., et al. (2021). Deficiency in X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein promotes susceptibility to microbial triggers of intestinal inflammation. Sci Immunol 6, eabf7473. DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abf7473
- Wahida, A., Muller, M., Hiergeist, A., Popper, B., Steiger, K., Branca, C., Tschurtschenthaler, M., Engleitner, T., Donakonda, S., De Coninck, J., Ollinger, R., Pfautsch, M.K., Muller, N., Silva, M., Usluer, S., Thiele Orberg, E., Bottcher, J.P., Pfarr, N., Anton, M., Slotta-Huspenina, J.B., Nerlich, A.G., Madl, T., Basic, M., Bleich, A., Berx, G., et al. (2021). XIAP restrains TNF-driven intestinal inflammation and dysbiosis by promoting innate immune responses of Paneth and dendritic cells. Sci Immunol 6, eabf7235. DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abf7235
- Eberl, C., Weiss, A.S., Jochum, L.M., Durai Raj, A.C., Ring, D., Hussain, S., Herp, S., Meng, C., Kleigrewe, K., Gigl, M., Basic, M., and Stecher, B. (2021). E. coli enhance colonization resistance against Salmonella Typhimurium by competing for galactitol, a context-dependent limiting carbon source. Cell Host Microbe. DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2021.09.004
- Roy, U., de Oliveira, R.S., Galvez, E.J.C., Gronow, A., Basic, M., Perez, L.G., Gagliani, N., Bleich, A., Huber, S., and Strowig, T. (2021). Induction of IL-22-Producing CD4+ T Cells by Segmented Filamentous Bacteria Independent of Classical Th17 Cells. Front Immunol 12, 671331. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.671331
- Kumari, S., Van, T.M., Preukschat, D., Schuenke, H., Basic, M., Bleich, A., Klein, U., and Pasparakis, M. (2021). NF-kappaB inhibition in keratinocytes causes RIPK1-mediated necroptosis and skin inflammation. Life Sci Alliance 4. DOI: 10.26508/lsa.202000956
- Basic, M., Bolsega, S., Smoczek, A., Glasner, J., Hiergeist, A., Eberl, C., Stecher, B., Gessner, A., and Bleich, A. (2021). Monitoring and contamination incidence of gnotobiotic experiments performed in microisolator cages. Int J Med Microbiol 311, 151482. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2021.151482
- Streidl, T., Karkossa, I., Segura Munoz, R.R., Eberl, C., Zaufel, A., Plagge, J., Schmaltz, R., Schubert, K., Basic, M., Schneider, K.M., Afify, M., Trautwein, C., Tolba, R., Stecher, B., Doden, H.L., Ridlon, J.M., Ecker, J., Moustafa, T., von Bergen, M., Ramer-Tait, A.E., and Clavel, T. (2021). The gut bacterium Extibacter muris produces secondary bile acids and influences liver physiology in gnotobiotic mice. Gut Microbes 13, 1-21. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1854008
- Fischer, F., Romero, R., Hellhund, A., Linne, U., Bertrams, W., Pinkenburg, O., Eldin, H.S., Binder, K., Jacob, R., Walker, A., Stecher, B., Basic, M., Luu, M., Mahdavi, R., Heintz-Buschart, A., Visekruna, A., and Steinhoff, U. (2020). Dietary cellulose induces anti-inflammatory immunity and transcriptional programs via maturation of the intestinal microbiota. Gut Microbes 12, 1-17. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1829962
- Willers, M., Ulas, T., Vollger, L., Vogl, T., Heinemann, A.S., Pirr, S., Pagel, J., Fehlhaber, B., Halle, O., Schoning, J., Schreek, S., Lober, U., Essex, M., Hombach, P., Graspeuntner, S., Basic, M., Bleich, A., Cloppenborg-Schmidt, K., Kunzel, S., Jonigk, D., Rupp, J., Hansen, G., Forster, R., Baines, J.F., Hartel, C., et al. (2020). S100A8 and S100A9 Are Important for Postnatal Development of Gut Microbiota and Immune System in Mice and Infants. Gastroenterology 159, 2130-2145 e2135. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.08.019
- van Best, N., Rolle-Kampczyk, U., Schaap, F.G., Basic, M., Olde Damink, S.W.M., Bleich, A., Savelkoul, P.H.M., von Bergen, M., Penders, J., and Hornef, M.W. (2020). Bile acids drive the newborn's gut microbiota maturation. Nat Commun 11, 3692. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-17183-8
- Riba, A., Hassani, K., Walker, A., van Best, N., von Zezschwitz, D., Anslinger, T., Sillner, N., Rosenhain, S., Eibach, D., Maiga-Ascofare, O., Rolle-Kampczyk, U., Basic, M., Binz, A., Mocek, S., Sodeik, B., Bauerfeind, R., Mohs, A., Trautwein, C., Kiessling, F., May, J., Klingenspor, M., Gremse, F., Schmitt-Kopplin, P., Bleich, A., Torow, N., et al. (2020). Disturbed gut microbiota and bile homeostasis in Giardia-infected mice contributes to metabolic dysregulation and growth impairment. Sci Transl Med 12. DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aay7019
- Tajik, N., Frech, M., Schulz, O., Schalter, F., Lucas, S., Azizov, V., Durholz, K., Steffen, F., Omata, Y., Rings, A., Bertog, M., Rizzo, A., Iljazovic, A., Basic, M., Kleyer, A., Culemann, S., Kronke, G., Luo, Y., Uberla, K., Gaipl, U.S., Frey, B., Strowig, T., Sarter, K., Bischoff, S.C., Wirtz, S., et al. (2020). Targeting zonulin and intestinal epithelial barrier function to prevent onset of arthritis. Nat Commun 11, 1995. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-15831-7
- Eberl, C., Ring, D., Munch, P.C., Beutler, M., Basic, M., Slack, E.C., Schwarzer, M., Srutkova, D., Lange, A., Frick, J.S., Bleich, A., and Stecher, B. (2019). Reproducible Colonization of Germ-Free Mice With the Oligo-Mouse-Microbiota in Different Animal Facilities. Front Microbiol 10, 2999. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02999
- Stolzer, I., Kaden-Volynets, V., Ruder, B., Letizia, M., Bittel, M., Rausch, P., Basic, M., Bleich, A., Baines, J.F., Neurath, M.F., Wirtz, S., Weidinger, C., Bischoff, S.C., Becker, C., and Gunther, C. (2020). Environmental Microbial Factors Determine the Pattern of Inflammatory Lesions in a Murine Model of Crohn's Disease-Like Inflammation. Inflamm Bowel Dis 26, 66-79. DOI: 10.1093/ibd/izz142
- Eftychi, C., Schwarzer, R., Vlantis, K., Wachsmuth, L., Basic, M., Wagle, P., Neurath, M.F., Becker, C., Bleich, A., and Pasparakis, M. (2019). Temporally Distinct Functions of the Cytokines IL-12 and IL-23 Drive Chronic Colon Inflammation in Response to Intestinal Barrier Impairment. Immunity 51, 367-380 e364. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.06.008
- Bolsega, S., Basic, M., Smoczek, A., Buettner, M., Eberl, C., Ahrens, D., Odum, K.A., Stecher, B., and Bleich, A. (2019). Composition of the Intestinal Microbiota Determines the Outcome of Virus-Triggered Colitis in Mice. Front Immunol 10, 1708. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01708
- Basic, M., and Bleich, A. (2019). Gnotobiotics: Past, present and future. Lab Anim 53, 232-243. DOI: 10.1177/0023677219836715
- Herp, S., Brugiroux, S., Garzetti, D., Ring, D., Jochum, L.M., Beutler, M., Eberl, C., Hussain, S., Walter, S., Gerlach, R.G., Ruscheweyh, H.J., Huson, D., Sellin, M.E., Slack, E., Hanson, B., Loy, A., Baines, J.F., Rausch, P., Basic, M., Bleich, A., Berry, D., and Stecher, B. (2019). Mucispirillum schaedleri Antagonizes Salmonella Virulence to Protect Mice against Colitis. Cell Host Microbe 25, 681-694 e688. DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2019.03.004
- Ring, C., Klopfleisch, R., Dahlke, K., Basic, M., Bleich, A., and Blaut, M. (2019). Akkermansia muciniphila strain ATCC BAA-835 does not promote short-term intestinal inflammation in gnotobiotic interleukin-10-deficient mice. Gut Microbes 10, 188-203. DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2018.1511663
- Fulde, M., Sommer, F., Chassaing, B., van Vorst, K., Dupont, A., Hensel, M., Basic, M., Klopfleisch, R., Rosenstiel, P., Bleich, A., Backhed, F., Gewirtz, A.T., and Hornef, M.W. (2018). Neonatal selection by Toll-like receptor 5 influences long-term gut microbiota composition. Nature 560, 489-493. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0395-5
- Kaden-Volynets, V., Basic, M., Neumann, U., Pretz, D., Rings, A., Bleich, A., and Bischoff, S.C. (2019). Lack of liver steatosis in germ-free mice following hypercaloric diets. Eur J Nutr 58, 1933-1945. DOI: 10.1007/s00394-018-1748-4
- Pezoldt, J., Pasztoi, M., Zou, M., Wiechers, C., Beckstette, M., Thierry, G.R., Vafadarnejad, E., Floess, S., Arampatzi, P., Buettner, M., Schweer, J., Fleissner, D., Vital, M., Pieper, D.H., Basic, M., Dersch, P., Strowig, T., Hornef, M., Bleich, A., Bode, U., Pabst, O., Bajenoff, M., Saliba, A.E., and Huehn, J. (2018). Neonatally imprinted stromal cell subsets induce tolerogenic dendritic cells in mesenteric lymph nodes. Nat Commun 9, 3903. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06423-7
- Basic, M., and Bleich, A. (2018). Gnotobiology. In The Gut Microbiome in Health and Disease, D. Haller, ed. (Springer).
- Basic, M., Buettner, M., Keubler, L.M., Smoczek, A., Bruesch, I., Buchheister, S., and Bleich, A. (2018). Loss of CD14 leads to disturbed epithelial-B cell crosstalk and impairment of the intestinal barrier after E. coli Nissle monoassociation. Sci Rep 8, 719. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-19062-7
- Wilck, N., Matus, M.G., Kearney, S.M., Olesen, S.W., Forslund, K., Bartolomaeus, H., Haase, S., Mahler, A., Balogh, A., Marko, L., Vvedenskaya, O., Kleiner, F.H., Tsvetkov, D., Klug, L., Costea, P.I., Sunagawa, S., Maier, L., Rakova, N., Schatz, V., Neubert, P., Fratzer, C., Krannich, A., Gollasch, M., Grohme, D.A., Corte-Real, B.F., …Basic, M., et al. (2017). Salt-responsive gut commensal modulates TH17 axis and disease. Nature 551, 585-589. DOI: 10.1038/nature24628
- Sunderhauf, A., Skibbe, K., Preisker, S., Ebbert, K., Verschoor, A., Karsten, C.M., Kemper, C., Huber-Lang, M., Basic, M., Bleich, A., Buning, J., Fellermann, K., Sina, C., and Derer, S. (2017). Regulation of epithelial cell expressed C3 in the intestine - Relevance for the pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease? Mol Immunol 90, 227-238. DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.08.003
- Thiemann, S., Smit, N., Roy, U., Lesker, T.R., Galvez, E.J.C., Helmecke, J., Basic, M., Bleich, A., Goodman, A.L., Kalinke, U., Flavell, R.A., Erhardt, M., and Strowig, T. (2017). Enhancement of IFNgamma Production by Distinct Commensals Ameliorates Salmonella-Induced Disease. Cell Host Microbe 21, 682-694 e685. DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2017.05.005
- Buchheister, S., Buettner, M., Basic, M., Noack, A., Breves, G., Buchen, B., Keubler, L.M., Becker, C., and Bleich, A. (2017). CD14 Plays a Protective Role in Experimental Inflammatory Bowel Disease by Enhancing Intestinal Barrier Function. Am J Pathol 187, 1106-1120. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2017.01.012
- Dupont, A., Sommer, F., Zhang, K., Repnik, U., Basic, M., Bleich, A., Kuhnel, M., Backhed, F., Litvak, Y., Fulde, M., Rosenshine, I., and Hornef, M.W. (2016). Age-Dependent Susceptibility to Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) Infection in Mice. PLoS Pathog 12, e1005616. DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005616
- Rausch, P., Basic, M., Batra, A., Bischoff, S.C., Blaut, M., Clavel, T., Glasner, J., Gopalakrishnan, S., Grassl, G.A., Gunther, C., Haller, D., Hirose, M., Ibrahim, S., Loh, G., Mattner, J., Nagel, S., Pabst, O., Schmidt, F., Siegmund, B., Strowig, T., Volynets, V., Wirtz, S., Zeissig, S., Zeissig, Y., Bleich, A., et al. (2016). Analysis of factors contributing to variation in the C57BL/6J fecal microbiota across German animal facilities. Int J Med Microbiol 306, 343-355. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2016.03.004
- Peuker, K., Muff, S., Wang, J., Kunzel, S., Bosse, E., Zeissig, Y., Luzzi, G., Basic, M., Strigli, A., Ulbricht, A., Kaser, A., Arlt, A., Chavakis, T., van den Brink, G.R., Schafmayer, C., Egberts, J.H., Becker, T., Bianchi, M.E., Bleich, A., Rocken, C., Hampe, J., Schreiber, S., Baines, J.F., Blumberg, R.S., and Zeissig, S. (2016). Epithelial calcineurin controls microbiota-dependent intestinal tumor development. Nat Med 22, 506-515. DOI: 10.1038/nm.4072
- Torow, N., Yu, K., Hassani, K., Freitag, J., Schulz, O., Basic, M., Brennecke, A., Sparwasser, T., Wagner, N., Bleich, A., Lochner, M., Weiss, S., Forster, R., Pabst, O., and Hornef, M.W. (2015). Active suppression of intestinal CD4(+)TCRalphabeta(+) T-lymphocyte maturation during the postnatal period. Nat Commun 6, 7725. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8725
- Rausch, P., Steck, N., Suwandi, A., Seidel, J.A., Kunzel, S., Bhullar, K., Basic, M., Bleich, A., Johnsen, J.M., Vallance, B.A., Baines, J.F., and Grassl, G.A. (2015). Expression of the Blood-Group-Related Gene B4galnt2 Alters Susceptibility to Salmonella Infection. PLoS Pathog 11, e1005008. DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005008
- Schaubeck, M., Clavel, T., Calasan, J., Lagkouvardos, I., Haange, S.B., Jehmlich, N., Basic, M., Dupont, A., Hornef, M., von Bergen, M., Bleich, A., and Haller, D. (2016). Dysbiotic gut microbiota causes transmissible Crohn's disease-like ileitis independent of failure in antimicrobial defence. Gut 65, 225-237. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309333
- Gunther, C., Buchen, B., He, G.W., Hornef, M., Torow, N., Neumann, H., Wittkopf, N., Martini, E., Basic, M., Bleich, A., Watson, A.J., Neurath, M.F., and Becker, C. (2015). Caspase-8 controls the gut response to microbial challenges by Tnf-alpha-dependent and independent pathways. Gut 64, 601-610. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307226
- Dannappel, M., Vlantis, K., Kumari, S., Polykratis, A., Kim, C., Wachsmuth, L., Eftychi, C., Lin, J., Corona, T., Hermance, N., Zelic, M., Kirsch, P., Basic, M., Bleich, A., Kelliher, M., and Pasparakis, M. (2014). RIPK1 maintains epithelial homeostasis by inhibiting apoptosis and necroptosis. Nature 513, 90-94. DOI: 10.1038/nature13608
- Basic, M., Keubler, L.M., Buettner, M., Achard, M., Breves, G., Schroder, B., Smoczek, A., Jorns, A., Wedekind, D., Zschemisch, N.H., Gunther, C., Neumann, D., Lienenklaus, S., Weiss, S., Hornef, M.W., Mahler, M., and Bleich, A. (2014). Norovirus triggered microbiota-driven mucosal inflammation in interleukin 10-deficient mice. Inflamm Bowel Dis 20, 431-443. DOI: 10.1097/01.MIB.0000441346.86827.ed